static navicular drop test|navicular drop normal range : trade The Navicular Drop Test (NDT) was first described by Brody in 1982 as a means of quantifying the amount of foot pronation in runners.It is the one of the static foot assessment tool and is intended to represent the sagittal plane displacement of the navicular tuberosity from a neutral position i.e. Subtalar joint . See more WEBAtive os 5 pilares do emagrecimento definitivo no seu corpo e emagreça como nunca treinando apenas 25 minutos por dia e podendo comer de tudo o que gosta todos os dias. . Desenvolvida por Guto Galamba, o Seca Todo Dia é baseado na Metodologia dos 5 Pilares do Emagrecimento Definitivo: Hidratação. Calculada. Alimentação Planejada.
{plog:ftitle_list}
26 de out. de 2023 · Por GIGA-SENA. O sorteio do concurso 2939 ocorreu no dia 26 de outubro de 2023 e o prêmio principal foi estimado em R$ 1.700.000,00 (um milhão e .
The Navicular Drop Test (NDT) was first described by Brody in 1982 as a means of quantifying the amount of foot pronation in runners.It is the one of the static foot assessment tool and is intended to represent the sagittal plane displacement of the navicular tuberosity from a neutral position i.e. Subtalar joint . See morePosition the patient in standing so there is full weight-bearing through the lower extremity and ensure the foot is in the subtalar joint neutral . See more
The function and structure of the medial longitudinal arch (MLA) of the foot has been proposed as a risk factor for developing injuries . See moreTable 1. NDT Values Table 2. Measurement of navicular height in standing Table 3. Performance of the NDT Foot length had a significant influence on the navicular drop in both men (p < 0.001) and women (p = 0.015), whereas no significant effect was . See more The results of the current study suggest that the change in dorsal arch height during the Sit-to-Stand test offers the clinician a reliable and valid .
The Navicular Drop Test is a test to assess for pes planus and overpronation which can be a factor in plantar fasciitis/heel pain.The navicular drop test is a measure to evaluate the function of the medial longitudinal arch, which is important for the examination of patients with overuse injuries. Conflicting results have been found with regard to differences in navicular drop between healthy and injured participants.Static navicular drop has been a relatively poor predictor of the navicular drop (ND) during walking . A dynamic navicular drop test was introduced by Cornwall and McPoil using a 6D .The navicular drop test (NDT) measures change in static navicular height (NH), but has variable reliability. Reliability has been affected by inconsistencies when finding subtalar joint.
The navicular drop test provides an objective measurement of the extent of plastic deformation in the support tissues. It is an easy-to-perform clinical test that requires no special equipment, . The navicular drop of 72 healthy runners was evaluated using 2 static methods. Results were used to classify individuals into groups and compared to dynamic measures of .
Brody introduced the static navicular drop test as a measure to evaluate MLA. In previous studies, mean values among healthy adults range from 3.6 to 8.1 mm in the original version of the test [ 17 – 21 ] and from 7.3 to 9.0 . The five criteria for recruitment of flatfoot participants were foot posture index (FPI), navicular drop test, stage I and II posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD), footprint, and . On the static navicular drop test, there were 3 studies for AI vs. PI, 5 studies for AI vs. control, and 1 study for PI vs. control group. All data were imported into R software, and direct and indirect comparisons were made with the random effect model. Control group was considered as one of the treatments.
The navicular drop test is a measure to evaluate the function of the medial longitudinal arch, which is important for examination of patients with overuse injuries. Conflicting results have been found with regard to differences .Objective: The aim was to determine the interrater and intrarater reliability of navicular drop (NDP), navicular drift (NDT), and the Foot Posture Index-6 (FPI-6), and test-retest reliability of the static arch index (SAI) and dynamic arch index (DAI). Methods: Sixty healthy individuals were assessed for intrarater and test-retest reliability.
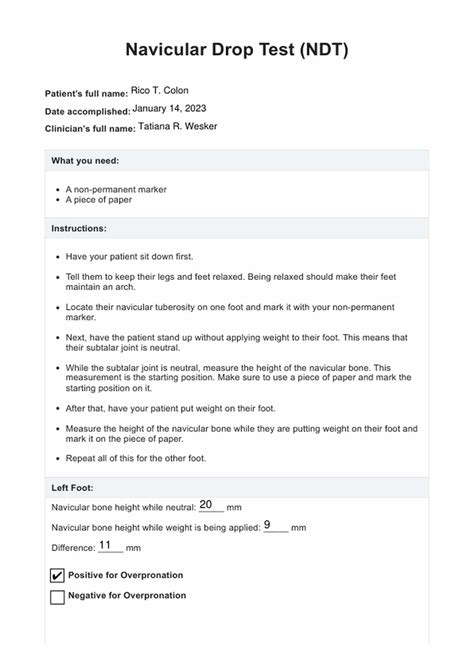
The navicular drop test is a common clinical measure of foot structure and, more specifically, of talonavicular joint function. Previous work has focused on static measurement to establish the relationship between navicular drop and various overuse injuries. However, loads on foot structure are dramatically increased during gait. Objective. The aim was to determine the interrater and intrarater reliability of navicular drop (NDP), navicular drift (NDT), and the Foot Posture Index-6 (FPI-6), and test–retest reliability of the static arch index (SAI) and dynamic arch index (DAI).The Navicular Drop Test is a test to assess for pes planus and overpronation. An increased navicular drop is associated with an increased risk of overuse injuries such as medial tibial stress syndrome, plantar fasciitis, as well as patellofemoral pain syndrome.The navicular drop is defined as the distance the navicular tuberosity moves in .
navicular drop test pdf
Conclusion: While the navicular drop test has been widely used as a clinical method to assess foot mobility, poor levels of inter-rater reliability have been reported. The results of the current study suggest that the change in dorsal arch height during the Sit-to-Stand test offers the clinician a reliable and valid alternative to the navicular . The navicular drop test (NDT) has been widely used as a clinical method to assess foot mobility. The NDT has also been associated with lower limb musculoskeletal injuries [1–3].Brody was one of the first to describe the NDT and he noted that it was helpful in evaluating the amount of foot mobility, specifically pronation, in runners [].Brody stated that the NDT was .
web gzip compression test
Study design: Controlled laboratory study using a cross-sectional design. Objectives: To compare the measurements of navicular drop during walking and running to those made clinically during a static position in a group of healthy young adults. Background: The navicular drop test is a common clinical measure of foot structure and, more specifically, of talonavicular joint function. The navicular drop was calculated by using the navicular drop test. Mean, standard deviation and Pearson correlation coefficient were calculated. Data was analyzed by using SPSS version 21.
• the relaxed position of the navicular drift and drop could be measured in the single limb stance positions. If measured and used for research – will need to control for foot length – larger feet will have larger amounts of navicular drift and drop. Cross check navicular drift with MTJ oblique axis clinical determination. Reliability – We found just one clinical measure, the navicular drop test, to be associated with injury. Unlike static measures such as Foot Posture Index, which was not found to be univariately related to . Brody introduced the static navicular drop (ND) test, which was meant as a quick clinical test to estimate foot pronation during dynamic conditions. However, how well static ND predicts dynamic ND during walking has never been investigated. The purpose of this study was to investigate how well static ND corresponds to dynamic measures of ND .Le navicular drop test décrit par Brody (Brody et al. 1982) en 1982, est l'un des tests cliniques les plus couramment utilisés pour étudier l’arche longitudinale médiale (Nguyen et al. 2009 ; Shultz et al. 2006). Il identifie la différence entre la hauteur de la tubérosité naviculaire dans l'articulation sous-talienne en position .
Group Classification. We screened subjects for foot type by measuring the degree of subtalar pronation using the navicular-drop test. Navicular drop was measured using a modification of the Brody method, 22 with the subject in a weight-bearing position. We asked the subject to stand barefoot on a 4-in (10.16-cm) box, placing all weight on the foot being measured, while the . The purpose of this study was to investigate: 1) the reliability of the stretch-sensor for measuring navicular drop, and 2) the concurrent validity of the stretch-sensor compared to the static . The navicular drop test is a method to assess the degree to which the talus plantar flexes in space on a calcaneus that has been stabilized by the ground. . midfoot, and rearfoot static alignment in pain-free individuals. J .Brody introduced the static navicular drop (ND) test, which was meant as a quick clinical test to estimate foot pronation during dynamic conditions. However, how well static ND predicts dynamic ND during walking has never been investigated. The purpose of this study was to investigate how well static ND corresponds to dynamic measures of ND .
Static foot assessment was undertaken using the Foot Posture Index (FPI-6), rearfoot angle (RFA), medial longitudinal arch angle (MLAA) and navicular drop (ND) in 30 participants (29 ± 6 years, 1.72 ± 0.08 m, 75 ± 18 kg). The right foot was measured on two occasions by one rater within the same test environment.Background: Understanding foot motion and function during activity is essential for clinicians because different foot types may require different treatment or rehabilitation strategies. Brody introduced the static navicular drop (ND) test, which was meant as a quick clinical test to estimate foot pronation during dynamic conditions. However, how well static ND predicts .
The navicular drop test (NDT) measures change in static navicular height (NH), but has variable reliability. Reliability has been affected by inconsistencies when finding subtalar joint neutral .
We have developed a stretch-sensor that allows for in-shoe measurement of navicular drop but the reliability and validity is unknown. The purpose of this study was to investigate: 1) the reliability of the stretch-sensor for measuring navicular drop, and 2) the concurrent validity of the stretch-sensor compared to the static navicular drop test.The footprint parameters had excellent correlation with each other (0.838-0.881). The navicular drop test and the footprint parameters studied were reproducible and thus had excellent reliability. . 34 and moderate correlation for the static AI (r = 0.44) and the dynamic AI (r = 0.570). 35 The AI is a measurement dependent on the contact area .
navicular drop test norms
The aim was to determine the interrater and intrarater reliability of navicular drop (NDP), navicular drift (NDT), and the Foot Posture Index-6 (FPI-6), and test–retest reliability of the static arch index (SAI) and dynamic arch index (DAI). Methods. Sixty healthy individuals were assessed for intrarater and test–retest reliability. Static navicular drop has been a relatively poor predictor of the navicular drop (ND) during walking . A dynamic navicular drop test was introduced by Cornwall and McPoil using a 6D electromagnetic motion analysis system. Among 106 healthy participants ND was found to be 5.9 mm (SD ± 2.8). The minimal markerset allows to simply transfer the known concepts of navicular drop and drift from quasi-static clinical test conditions to functional tasks, which is recommended to more closely .
The second static test – the static subtalar navicular drop test – compares navicular height when the foot is placed in “neutral” position to when the foot is allowed to relax and compress the arch. Results of Dicharry’s study (see below) showed that despite significant differences in arch collapse between the groups during static .
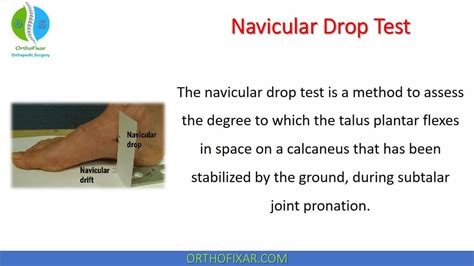
navicular drop test normal values
Byblos (/ ˈ b ɪ b l ɒ s / BIB-loss; Greek: Βύβλος), also known as Jebeil, Jbeil or Jubayl (Arabic: جُبَيْل, romanized: Jubayl, locally Jbeil; Phoenician: 𐤂𐤁𐤋, GBL, probably Gebal), is an ancient city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon.The area is believed to have been first settled between 8800 and 7000 BC and continuously inhabited since 5000 BC.
static navicular drop test|navicular drop normal range